Want to inspire change in scientific research? Check out the 25 best open science initiatives and practices.
Traditional “closed” scientific research often limits access to knowledge and stifles productivity in research.
Open science offers a potential solution to these problems.
It is a promising solution that encourages researchers to share their findings, data, and methods, fostering collaboration, transparency, and innovation.
Table of Contents
Overview
Open science initiatives aim to create a more collaborative and transparent research environment, fostering innovation, efficiency, and accessibility to knowledge.
Open science promotes researchers’ career growth and streamlines access to research tools for replication. It also ensures fair knowledge dissemination, benefiting the scientific community and the public.
In this blog post, we highlight the 25 best open science initiatives and practices that researchers and academia can adopt.
Best Open Science Initiatives and Practices
#1. Open Access Publishing: Best for Broad Dissemination of Research

Summary
- Ensures free and unrestricted access to published research
- Removes paywalls and embargos
- Promotes wide dissemination of research findings
Open access publishing enables researchers to publish their work in a manner that anyone can access, read, and share without financial or legal barriers.
Examples of organizations advocating for open access publishing are the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ) and PLOS (Public Library of Science).
What are the benefits of Open Access?
- Wider audience reach: Research articles are available to a larger audience without subscription barriers.
- Faster publication process: Reduced time from submission to publication due to streamlined editorial workflows.
- Increased citation rates: Unrestricted access to articles leads to increased citation by other researchers.
Open access publishing is a fundamental practice in open science that dramatically improves the visibility and accessibility of research findings.
Source: https://guides.library.cornell.edu/openaccess
#2. Pre-Print Repositories: Best for Instant and Open Publication of Manuscripts

Summary
- Enables early sharing of research findings
- Facilitates feedback from the scientific community
- Allows for citation of pre-published work
Pre-print repositories allow researchers to share their manuscripts before they are formally published, enabling rapid dissemination of research findings and valuable feedback from peers. Some of these pre-print repositories include arXiv, bioRxiv, and SSRN.
What are the benefits of Pre-Print Repositories?
- Quick dissemination of research: Manuscripts are available online immediately after submission.
- Early feedback from the community: Researchers can provide input and suggestions to authors prior to formal publication.
- Visibility and discoverability of work: Pre-print repositories increase exposure for research even before the final, published version.
Pre-print repositories foster knowledge sharing and scientific collaboration, speeding up scientific advancements in a transparent and open manner.
Source: https://www.enago.com/academy/why-researchers-should-use-pre-print-repositories/
#3. Open Data Repositories: Best for Sharing and Reusing Raw Research Data

Summary
- Encourages sharing of raw research data
- Reduces duplication of efforts and resource waste
- Facilitates reproducibility of findings
Open data repositories provide a platform for researchers to share raw research data, allowing other researchers to access, use, and build upon their work. Dryad, Figshare, and Zenodo are three examples of open data repositories.
What are the benefits of Open Data Repositories?
- Facilitates data sharing and reuse: Data can be uploaded, accessed, and reused by other researchers.
- Encourages replicability and transparency: Availability of data enables verification and reproduction of research findings.
- Stimulates new research opportunities: Open data encourages interdisciplinary research and novel hypothesis testing.
Sharing raw research data through open data repositories enhances the integrity and reproducibility of scientific findings, promoting cooperation and trust among researchers.
Source: https://www.opendatarepository.org/
#4. Data Management Plans: Best for Organizing, Storing, and Handling Research Data
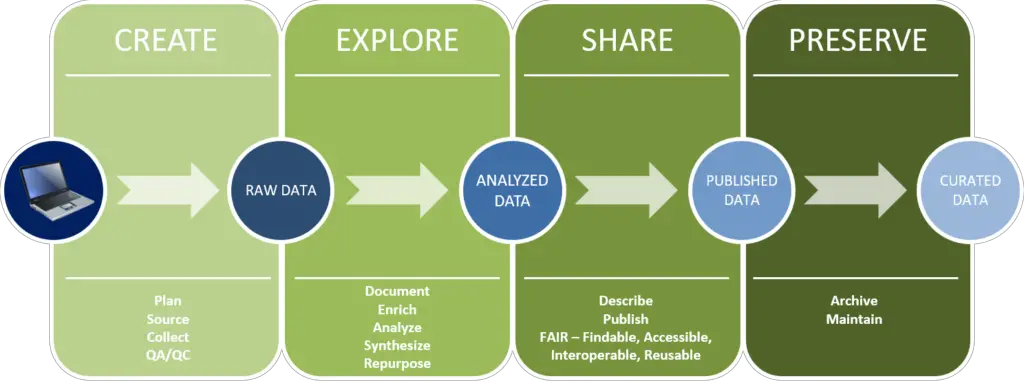
Summary
- Provides a systematic approach to organizing and storing research data
- Ensures long-term preservation and accessibility of data
- Complies with funding agency requirements
Data management plans (DMPs) are essential tools for researchers to organize, store, and handle research data throughout a project’s lifecycle. DMPs help researchers ensure that their data is preserved and accessible, complying with requirements from funding agencies.
What are the benefits of Data Management Plans?
- Improved data organization: Effective management of research data enhances productivity and data sharing.
- Secure storage and backup: DMPs ensure proper data storage, preservation, and retrieval.
- Simplified data retrieval: Researchers can easily locate and access relevant data with a well-implemented DMP.
Proper data management planning enables researchers to make the most of their data, ensuring transparency, reproducibility, and maximum research impact.
Source: https://library.stanford.edu/research/data-management-services/data-management-plans
#5. Open Source Software: Best for Collaborative Development of Useful Software

Summary
- Encourages collaboration in software development
- Provides free access to high-quality software tools
- Allows customization and improvement of software tools
Open source software is software that is developed, tested, and improved through collaborative efforts, and it is publicly accessible for anyone to use, modify, or distribute.
Examples of open source software in research include R (a statistical programming language), Jupyter Notebooks (for document sharing), and Open Science Framework (OSF).
What are the benefits of Open Source Software?
- Collaborative development: Open source software encourages contributions from a diverse community of developers.
- Cost-effective solution: Free access to valuable software reduces overall research and development costs.
- Continuous software improvement: The open nature of the software promotes continuous development and enhancement.
Open source software promotes collaborative development and sharing of powerful research tools, fostering innovation and efficiency in the scientific community.
Source: https://opensource.com/resources/what-open-source
#6. Code Repositories: Best for Version Control and Collaboration on Code

Summary
- Facilitates collaboration on code
- Provides version control features
- Enhances transparency and reproducibility in research
Code repositories like GitHub allow researchers to host, share, and collaborate on code, making programming projects more transparent and easily reproducible. They provide version control tools that preserve the evolution of the code and enhance collaboration among contributors.
What are the benefits of Code Repositories?
- Efficient version control: Code repositories track changes, allowing for effective management of multiple versions.
- Simplified collaboration on projects: Multiple contributors can work on code simultaneously, streamlining development.
- Easier code tracking and management: Centralized storage and organization of code simplifies project tracking.
Code repositories enhance transparency, collaboration, and reproducibility in computational research projects.
Source: https://www.sonatype.com/launchpad/what-are-code-repositories
#7. Research Collaboration Platforms: Best for Scientific Networking and Collaboration

Summary
- Connects researchers from around the world
- Shares research findings, data, and tools
- Facilitates collaboration opportunities
Research collaboration platforms like ResearchGate enable researchers to network, share research findings, and collaborate on projects. These platforms foster a global research community focused on knowledge exchange and cooperation.
What are the benefits of Research Collaboration Platforms?
- Networking and collaboration opportunities: Provides researchers with a platform to connect and collaborate on projects.
- Personalized content and recommendations: Tailored suggestions based on research interests and profile.
- One platform for research and publication management: Allows for efficient management of publications and research projects
Research collaboration platforms foster an interconnected research community, promoting innovation and collaboration on a global scale.
Source: https://libguides.mit.edu/c.php?g=695148&p=4986638
#8. Open Peer Review: Best for Transparency and Quality Control of Research Output
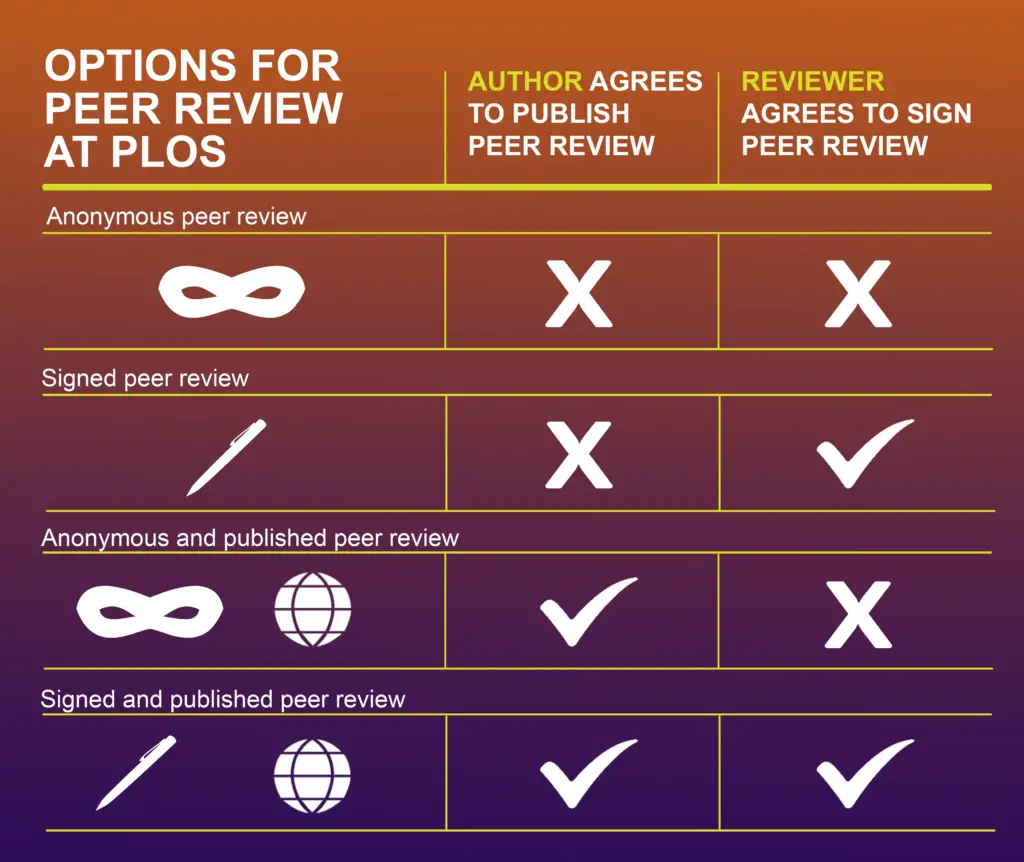
Summary
- Provides transparent, constructive review processes
- Enhances reviewer accountability and recognition
- Reduces bias in the review process
Open peer review involves the transparent and accessible sharing of peer review reports and reviewer identities, promoting a more equitable and accountable review process.
This practice fosters quality control and impartiality in evaluating research outputs, such as articles and grant proposals.
What are the benefits of Open Peer Review?
- Increased transparency: Open peer review promotes transparency and trust in the review process.
- Constructive criticism: Open discourse allows researchers to provide feedback and improve research outcomes.
- Reduced bias: Open communication enables fair assessment of research, fostering equality and diversity.
Open peer review enhances the quality and integrity of research outputs, fostering trust and accountability in the scientific community.
Source: https://plos.org/resource/open-peer-review/
#9. Citizen Science: Best for Involvement of Public in Research Process
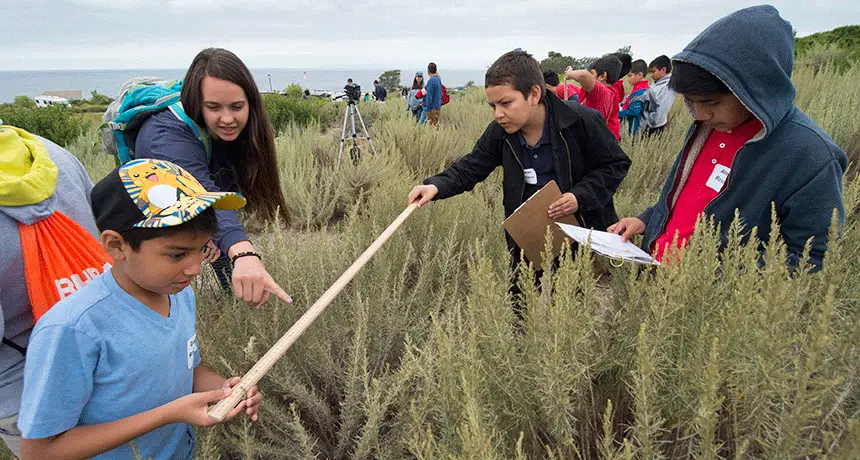

Summary
- Engages the public in scientific research
- Provides valuable data resources
- Enhances science literacy among the general public
Citizen science projects involve the participation of non-professional individuals in collecting, analyzing, or interpreting data for scientific research.
These projects contribute valuable data and perspectives to research while raising awareness and enthusiasm for science among the general public.
What are the benefits of Citizen Science?
- Engaged public involvement: Invites individuals from various backgrounds to participate in and contribute to research.
- Access to diverse perspectives: Enriches scientific understanding through the unique knowledge of non-experts.
- Enhanced data collection: Engages citizens in data collection efforts, resulting in larger and more diverse datasets.
Citizen science bridges the research community and the general public, leveraging the power of collective knowledge and fostering an inclusive and vibrant scientific ecosystem.
Source: https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/citizen-science/
#10. Open Educational Resources (OER): Best for Accessibility of Quality Teaching Resources

Summary
- Provides free access to high-quality educational resources
- Enables customization and improvement of learning materials
- Reduces costs for educational institutions
Open educational resources (OER) are freely accessible, openly licensed materials that can be used, adapted, and redistributed for teaching purposes. Examples of OER include online textbooks, video lectures, and educational software.
What are the benefits of Open Educational Resources?
- Free access to educational materials: OER reduces barriers to learning for students and educators.
- Customizable content: Instructors and learners can tailor materials to suit their needs.
- Peer-reviewed quality assurance: Open resources undergo rigorous quality assessment, ensuring accuracy and relevance.
OER promotes equitable access to high-quality teaching materials, fostering collaboration and innovation in education and research.
Source: https://oercommons.org/
#11. Open Research Notebooks: Best for Real-time Sharing of Scientific Process

Summary
- Share research ideas, methodologies, and preliminary results.
- Platforms such as Open Science Framework and Jupyter Notebooks support open research notebooks.
- Facilitates collaboration and constructive feedback.
Open research notebooks offer a real-time platform for documenting and sharing scientific ideas, methodologies, and preliminary results. Researchers can collaborate and provide feedback on one another’s work for better and faster progress.
Open Science Framework and Jupyter Notebooks are examples of platforms that support open research notebooks.
What are the benefits of Open Research Notebooks?
- Collaborative research opportunities: Researchers can share their in-progress findings, facilitating collaboration.
- Open and transparent methodology: Promotes transparency and trust in the research process.
- Instant feedback and input: The research community can contribute suggestions and improvements in real time.
Open Research Notebooks serve as a hallmark of open science practices, paving the way for a transparent, collaborative, and openly accessible scientific process.
Source: https://openlabnotebooks.org/
#12.Open Licensing: Best for Free and Legal Sharing of Work

Summary
- Legal framework for sharing research outputs.
- Creative Commons licenses are widely used.
- Promotes accessible and reusable research materials.
Open licensing provides a legal framework for researchers to freely share their work, such as articles, data sets, and software.
Creative Commons licenses are a common choice for researchers sharing their work under open licensing terms, allowing others to reuse research materials for various purposes.
What are the benefits of Open Licensing?
- Simplified sharing of resources: Open licenses encourage sharing, reuse, and adaptation of content.
- Legal protection for creators: Provides authors with control over the use of their work while promoting sharing.
- Encouragement of reuse and remixing: Fosters innovation and creativity by allowing new interpretations of existing work.
Open licensing, particularly through platforms like Creative Commons, significantly contributes to the democratization of knowledge by making research readily shareable, accessible and legally protected.
Source: https://open.bccampus.ca/what-is-open-education/what-are-creative-commons-and-open-licences/
#13. Reproducible Research Practices: Best for Reliability and Verifiability of Research
Summary
- Research workflows are transparent and open-sourced.
- Ensures the reliability and verifiability of results.
- Tools include open-source software and version control systems.
Reproducible research practices involve maintaining open-sourced and transparent research workflows. This makes it easier for other researchers to reproduce experiments and validate findings. Examples of tools that promote reproducibility include R and Git.
What are the benefits of Reproducible Research Practices?
- Enhanced research reliability: Sharing scripts, methods, and datasets ensures that research findings are robust and trustworthy.
- Verification of results: Making research materials accessible allows others to independently confirm research outcomes.
- Increased scientific credibility: Reproducibility fosters confidence in the overall quality of research.
Reproducible research practices underpin a reliable and efficient scientific environment by promoting open-sourced workflows, verifiable results, and collaborative efforts among researchers.
Source: https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010750
#14. FAIR Data Principles: Best for Data Accessibility and Usability
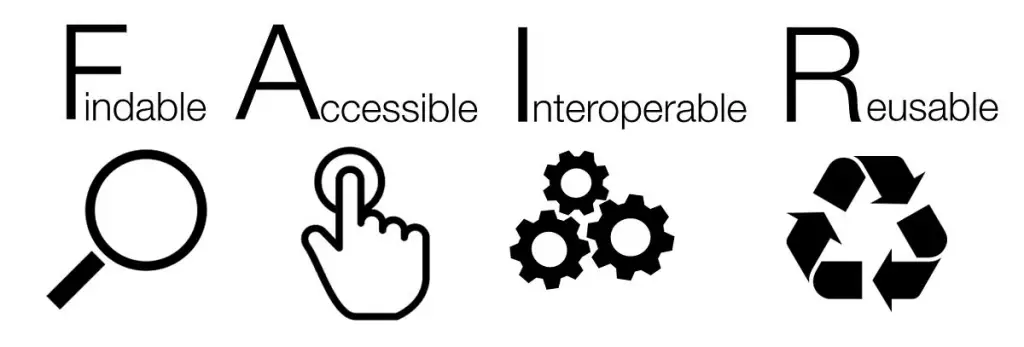
Summary
- Principles that promote Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable data.
- Makes data management more systematic and efficient.
- Encourages sharing data and simplifying data discovery.
FAIR Data Principles advocate for scientific data to be Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable. These principles guide researchers in making their data more easily discoverable, accessible, and usable, promoting open science and collaboration among researchers.
What are the benefits of FAIR Data Principles?
- Findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable data: Ensures that data is managed and shared according to best practices.
- Improved data discoverability and use: FAIR data is easier to find and utilize, promoting data-driven research.
- Standardized data management practices: Implementing FAIR principles assures consistency and efficiency across research efforts.
The realization of FAIR Data Principles embodies a pivotal stride towards a more accessible and user-friendly scientific field, ensuring not just data management efficiency but also championing discoveries and collaborations through seamless data sharing.
Source: https://www.go-fair.org/fair-principles/
#15. Open Metadata Standards: Best for Consistency and Efficiency in Data Organization

Summary
- Consistent data organization and documentation.
- Makes data sharing and discovery more efficient.
- Examples include Dublin Core, DataCite, and schema.org.
Open metadata standards ensure the consistency and efficiency of data organization across various repositories. Following best practices in organizing and documenting research data helps researchers share and discover data more efficiently.
Standards such as Dublin Core, DataCite, and schema.org are commonly used to achieve this.
What are the benefits of Open Metadata Standards?
- Consistent data organization: Common standards for metadata enable compatibility between datasets.
- Streamlined data sharing: Open metadata facilitates the exchange and integration of data.
- Easier data discoverability: Clear and consistent metadata guides users to relevant and useful data.
Open metadata standards fortify consistent data organization, fostering efficient data sharing, discovery, and promoting cross-disciplinary collaboration through recognized standards such as Dublin Core, DataCite, and schema.org.
Source: https://open-metadata.org/
#16. Open Science Training Programs: Best for Encouraging Open Science Practices

Summary
- Training programs on open science practices.
- Helps researchers adopt open science initiatives.
- Programs include CARP, FORCE11, and GO FAIR.
Open science training programs educate researchers on the many facets of open science initiatives and practices. These programs aim to help researchers become aware of and adopt open science methodologies in their work. CARP, FORCE11, and GO FAIR are examples of organizations offering open science training.
What are the benefits of Open Science Training Programs?
- Increased adoption of open practices: Training programs raise awareness and promote the benefits of open science.
- Skill development and learning resources: Provides researchers with tools and guidance needed to adopt open science practices.
- Community-building: Fosters a supportive network of open science practitioners.
By delivering valuable training on open science practices, programs like CARP, FORCE11, and GO FAIR not only bolster researchers’ understanding and adoption of these methodologies, but also stimulate the growth of a global open science community.
Source: https://www.cos.io/services/training
#17. Open Science Conferences and Workshops: Best for Sharing Ideas and Networking

Summary
- Events that promote open science practices.
- Encourage collaboration and networking among researchers.
- Examples include Open Science FAIR and Open Repositories conferences.
Open science conferences and workshops serve as platforms to share ideas, best practices, and new developments in open science. Researchers can connect with others who promote open science and become familiar with the latest tools and resources.
Events such as the Open Science FAIR and Open Repositories conferences are popular venues for sharing and networking.
What are the benefits of Open Science Conferences and Workshops?
- Exchange of knowledge and best practices: Conferences and workshops showcase current trends and research developments.
- Networking opportunities: Attendees meet and connect with like-minded peers and experts in the field.
- Inspiration for new research ideas: Exposure to a diverse range of work sparks innovation and collaboration.
Open science conferences and workshops, such as the Open Science FAIR and Open Repositories, fuel scientific progress by fostering networking, encouraging the dissemination of innovative ideas, and promoting learning within the open science community.
Source: https://www.un.org/en/library/OS23
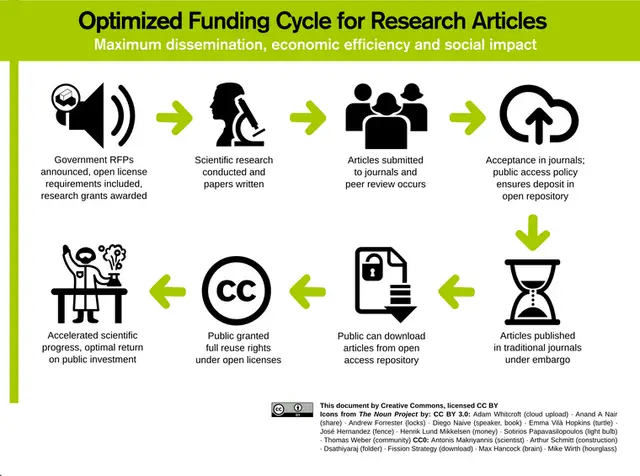
#18. Open Science Funding Sources: Best for Supporting Open Research Projects
Summary
- Financial support for open research projects.
- Enables researchers to adopt open science practices.
- Examples include OpenAIRE and OpenScapes.
Open science funding sources provide financial support for researchers pursuing open research projects.
These funding sources help researchers adopt open science practices and make their research outputs openly accessible. OpenAIRE and OpenScapes are examples of organizations that provide funding for open science projects.
What are the benefits of Open Science Funding Sources?
- Financial support for open projects: Ensures that open research initiatives have access to necessary resources.
- Encouragement of open science practices: Funding requirements drive adherence to open principles.
- Enhanced visibility for funded projects: Openly funded projects garner additional interest and attention.
Open science funding sources are instrumental in promoting open research projects. They offer financial support, foster the adoption of open science practices, and enhance the visibility of open scientific outputs.
Source: https://chanzuckerberg.com/science/programs-resources/open-science/grants/
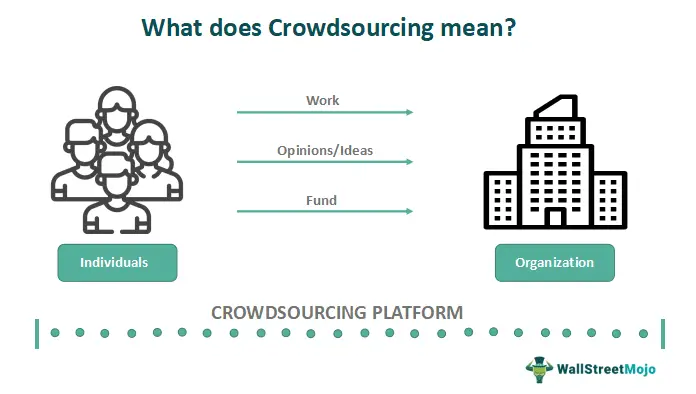
#19. Crowdsourcing Research Ideas: Best for Democratization of Science
Summary
- Involves seeking ideas and input from the scientific community.
- Promotes collaborative research and idea sharing.
- Examples include Innocentive and Kaggle.
Crowdsourcing research ideas allows researchers to seek input and ideas from a wider scientific community, increasing collaboration and democratizing the research process.
Platforms such as Innocentive and Kaggle enable researchers to engage with diverse perspectives and expertise.
What are the benefits of Crowdsourcing Research ideas?
- Inclusive idea generation: Diversity of input leads to innovative research questions and directions.
- Accelerated scientific innovation: Opens up new avenues of exploration by engaging a broader range of contributors.
- Increased public engagement: Empowers citizens to play an active role in driving scientific progress.
With platforms like Innocentive and Kaggle, crowdsourcing research ideas serves as a vehicle for democratizing science, stimulating idea exchange and collaboration among researchers, and facilitating access to an extensive pool of expertise.
#20. Open Science Advocacy Organizations: Best for Promoting Open Science

Summary
- Promote and support open science practices.
- Advocate for open access policies.
- Examples include SPARC, Right to Research, and Open Knowledge International.
Open science advocacy organizations work to create broader awareness of open science practices and advocate for policies that promote open access to research.
SPARC, Right to Research, and Open Knowledge International are examples of organizations that champion open science across various disciplines.
What are the benefits of Open Science Advocacy
- Lobbying for open science policies: Advocacy organizations work to influence decisions and shape policy in favor of open science.
- Creation of open science resources: Advocates provide information and support for the adoption of open practices.
- Encouragement of open practices within the research community: Fosters a culture of transparency and collaboration in the scientific community.
Open science advocacy organizations like SPARC, Right to Research, and Open Knowledge International spearhead the promotion of open science, bolstering awareness, advocating for open access policies, and supporting the broadening of open science initiatives.
https://oad.simmons.edu/oadwiki/Advocacy_organizations_for_OA
#21. Open Science Impact Metrics: Best for Quantifying Influence of Open Science

Summary
- Facilitate the assessment of open science impact
- Provide alternative metrics to traditional citation counts
- Measure and hold researchers accountable for their open science contributions
Open Science Impact Metrics aim to quantify the influence of open science initiatives. Focusing on alternative metrics complements traditional citation-based indicators like the impact factor.
Some examples of organizations and tools supporting this initiative include Altmetric, Plum Analytics, and ImpactStory.
What are the benefits of Open Science Impact Metrics?
- Improved understanding of open science impact: New metrics provide a comprehensive picture of the influence of open research outputs.
- Comprehensive assessment of research outputs: Alternative metrics take into account a broader range of research contributions.
- Support for open research career advancement: Recognition of open science achievements adds value in career development.
Open Science Impact Metrics play a crucial role in determining the widespread adoption of open science practices while providing quantifiable evidence of their benefits.
Source: https://www.fosteropenscience.eu/foster-taxonomy/open-metrics-and-impact
#22. Open Research Tools and Technologies: Best for Streamlining and Enhancing Scientific Process
Summary
- Provide free access to tools and resources
- Streamline research processes
- Enable more efficient and accurate analysis
Open research tools and technologies, like Jupyter Notebooks and GitHub, enable researchers to access and utilize resources to improve the quality and efficiency of their work.
They help researchers store, manage, and analyze data and document their methods for others to replicate or develop further.
What are the benefits of Open Research Tools and Technologies?
- Efficient research processes: Open tools lower barriers to entry and reduce redundancies in research workflows.
- Cost-effective and accessible tools: Free or low-cost options make research tools widely accessible.
- Collaborative technology development: Open source development drives software improvement and shared ownership of tools.
Open research tools and technologies empower researchers and contribute to the acceleration of scientific progress.
Source: https://research-fosdem.github.io/
#23. Open Data Tools: Best for Data Analysis and Visualization

Summary
- Simplify data analysis and visualization
- Facilitate collaboration and sharing of data sets
- Enhance research reproducibility and transparency
Open data tools, such as R, Python, and Tableau Public, allow researchers to manage, analyze, and visualize data effectively. They enable the sharing of data sets, making it easier for others to reproduce research findings or build upon them.
What are the benefits of Open Data Tools?
- Simplified data analysis: Software and tools streamline the process of analyzing and interpreting data.
- Engaging data visualization: Compelling visuals enhance communication of research results and insights.
- Enhanced data discoverability and sharing: Open data tools promote data availability and reuse.
Open data tools enhance the reliability and transparency of research while promoting collaboration and data sharing.
Source: https://codeforaotearoa.github.io/
#24. Open Digital Libraries: Best for Preserving and Providing Access to Digital Content

Summary
- Preserve and make accessible a range of digital content
- Enable the dissemination of research and knowledge
- Support lifelong learning and research
Open digital libraries, like the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ), provide free access to valuable knowledge resources. Researchers can disseminate their work, and academia can access research articles without paywalls.
What are the benefits of Open Digital Libraries?
- Streamlined access to digital resources: Centralized repositories facilitate ease of searching and retrieval.
- Preservation of digital materials: Ensures the long-term availability of valuable resources for future researchers.
- Support for interdisciplinary research: Brings together resources spanning a wide range of disciplines and subjects.
Open digital libraries play a vital role in ensuring the preservation and accessibility of scientific knowledge.
Source: https://openlibrary.org/
#25. Open Science Discussion Forums: Best for Rich and Informed Discussions on Open Science

Summary
- Create spaces for open and in-depth discussions on open science topics
- Encourage researchers to exchange experiences, opportunities, and challenges
- Raise awareness about best practices and developments in open science
Open science discussion forums, such as Reddit’s r/Open_Science and the Open Science MOOC, provide platforms for researchers and academics to engage in meaningful conversations and share best practices in open science.
What are the benefits of Open Science Discussion Forums?
- Knowledge exchange: Spaces for open discussion promote the sharing of insights and information among researchers.
- Opportunity for constructive debate: Critical analysis and dialogue improve research quality and understanding.
- Active engagement with diverse perspectives: Encourages an inclusive, collaborative approach to research and innovation.
Open science discussion forums provide valuable spaces where researchers can engage in rich and informed conversations about open science practices.
Source: https://www.eventbrite.com/cc/civica-research-open-science-discussion-forum-1443239
Conclusion
This blog post has shed light on the remarkable open science initiatives driving scientific progress. From the universal accessibility ensured by OpenAIRE to reproducibility accelerated by Reproducibility Project, the landscape of scientific research is evolving.
This evolution, characterized by inclusivity, transparency, and collaboration, sets the foundation for the future of scientific inquiry embellished by open science practices.